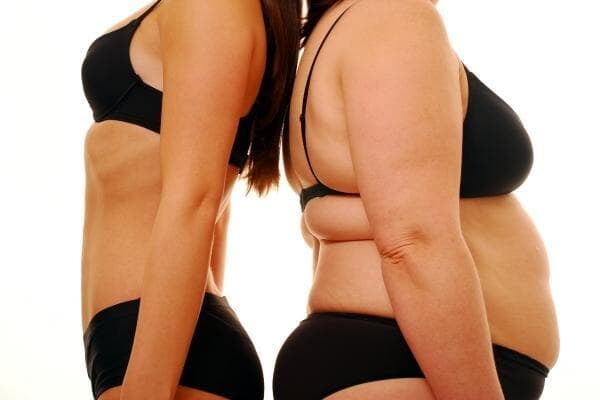
The Impact of Obesity on Physical Health:`
Obesity is a significant health concern that has detrimental effects on physical health. Excess body weight puts strain on the musculoskeletal system, leading to an increased risk of joint pain, osteoarthritis, and mobility issues. Furthermore, obesity is linked to an increased likelihood of developing chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease.
The impact of obesity on physical health extends beyond the alarming rise in chronic conditions. Individuals who are obese may also experience decreased quality of life due to limitations in physical function and reduced energy levels. Additionally, obesity can exacerbate existing health conditions, making management and treatment more challenging for healthcare providers.
Health Risks Associated with Obesity:
Obesity poses a myriad of health risks that can significantly impact an individual's well-being. Excess body weight is closely linked to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as the body may become resistant to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. This can result in serious complications such as nerve damage, kidney problems, and eye issues if left unmanaged.
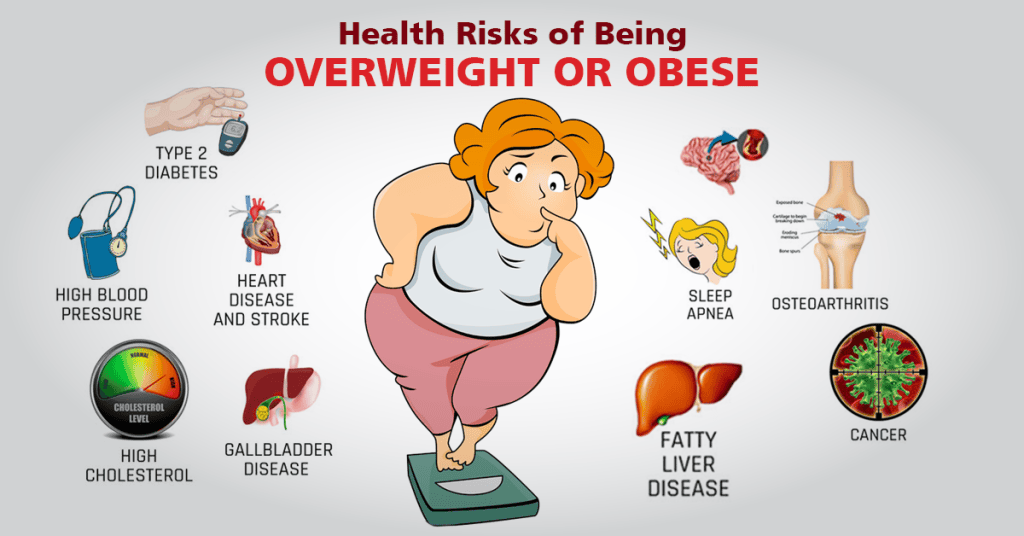
Moreover, carrying excess weight can also lead to high blood pressure, putting a strain on the heart and increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. The presence of additional fat tissue can contribute to inflammation in the body, which may further exacerbate heart-related issues. Additionally, obesity is associated with high levels of cholesterol and triglycerides, which can contribute to the build-up of plaque in the arteries, potentially leading to heart attacks and strokes.
Effects of Obesity on Mental Health:
Obesity is not only detrimental to physical health but also carries significant consequences for mental well-being. Individuals struggling with obesity often experience low self-esteem and negative body image, which can contribute to feelings of depression and anxiety. The societal stigma attached to being overweight can further exacerbate mental health issues, leading to social withdrawal and a sense of isolation.
Moreover, research has shown a strong association between obesity and cognitive decline. Excess body weight has been linked to impairments in memory, attention, and executive function. This cognitive decline can impact daily functioning and quality of life, adding an additional layer of challenges to those already struggling with the physical effects of obesity.
Obesity and Chronic Diseases:
- Obesity is a significant risk factor for the development of various chronic diseases.
- The excessive accumulation of body fat can lead to conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia.
- These chronic diseases not only impact the individual's quality of life but also pose a burden on the healthcare system.
- Managing obesity is crucial in preventing the onset and progression of these chronic illnesses.
- Furthermore, obesity is closely linked to the development of cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease, stroke, and heart failure.
- The excess weight places strain on the heart and blood vessels, leading to increased blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and inflammation.
- Individuals who are obese are at a higher risk of experiencing cardiovascular events and may require more intensive medical interventions to manage their condition.
- Addressing obesity through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions is essential in reducing the burden of chronic diseases on both individuals and society.
Obesity and Cardiovascular Health:
- Obesity is a significant risk factor for the development of cardiovascular diseases.
- Excess body weight can lead to the accumulation of fatty deposits in the arteries, causing them to narrow and harden, a condition known as atherosclerosis.
- This can restrict blood flow to the heart, leading to an increased risk of heart attacks and other heart-related problems.
- Furthermore, obesity is often associated with elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood, as well as high blood pressure.
- These factors can contribute to the development of conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, and stroke.
- It is crucial for individuals who are overweight or obese to take proactive steps to manage their weight and reduce their risk of cardiovascular issues.
The Link Between Obesity and Cancer:
Obesity has been identified as a significant risk factor for various types of cancer. Studies have shown that excess body weight can promote the growth of cancer cells and increase the likelihood of cancer development. The mechanisms behind this relationship are complex, involving hormonal imbalances, chronic inflammation, and changes in the body's metabolism and immune function.
Specifically, obesity has been linked to an increased risk of developing certain types of cancer, including breast, colon, prostate, and pancreatic cancer. The excess fat tissue in the body can release hormones such as estrogen and insulin, which can stimulate the growth of cancer cells. Additionally, obesity is associated with higher levels of inflammation in the body, which can create an environment conducive to cancer development and progression.
Obesity and Respiratory Health:
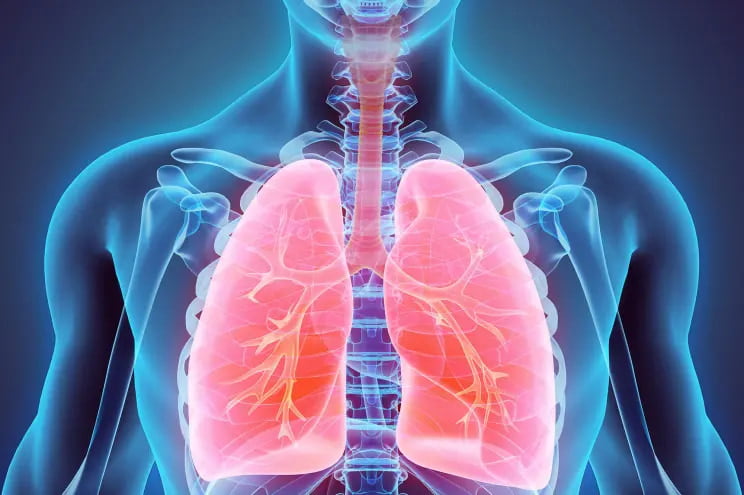
One of the significant health impacts of obesity is its negative effect on respiratory health. Excess body weight can lead to reduced lung function and capacity, making it more difficult for individuals to breathe effectively. This can result in symptoms such as shortness of breath, wheezing, and a higher risk of developing respiratory conditions like asthma and sleep apnea. Additionally, obesity can worsen existing respiratory conditions and make them harder to manage.
Furthermore, excess fat tissue in the chest and abdominal areas can put pressure on the lungs and diaphragm, further impeding lung function and respiratory efficiency. This can lead to a decrease in oxygen intake and impair the body's ability to adequately exchange gases in the lungs, leading to respiratory issues and potentially more severe complications. Maintaining a healthy weight through proper diet and regular physical activity is crucial in promoting optimal respiratory health and reducing the risk of developing respiratory conditions associated with obesity.
Obesity and Digestive Health:
Obesity is closely linked to various digestive health issues, impacting the overall functioning of the digestive system. The excess weight associated with obesity can put pressure on the stomach and intestines, leading to conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and heartburn. Furthermore, obesity is known to increase the risk of developing gallstones, as the excessive fat in the body can disturb the balance of cholesterol in the bile, leading to the formation of stones in the gallbladder.
Moreover, individuals who are obese are more likely to experience non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. NAFLD can progress to more severe forms of liver disease, such as steatohepatitis and cirrhosis, if left unmanaged. Additionally, obesity is a significant risk factor for developing pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas that can cause severe abdominal pain, digestive issues, and even lead to life-threatening complications.
Obesity and Reproductive Health:
Obesity can have a significant impact on reproductive health in both men and women. In women, obesity is linked to menstrual irregularities, such as irregular ovulation or even complete absence of menstruation. This can make it difficult for women to conceive and may lead to infertility issues. Additionally, obese women are at higher risk of developing conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which can further complicate fertility options.
In men, obesity can affect reproductive health by lowering testosterone levels and sperm quality. Excess body fat can disrupt hormone balance, leading to decreased sperm production and motility. This can increase the likelihood of male infertility and also impact sexual function. Furthermore, obesity in men has been associated with a higher incidence of erectile dysfunction, which can further hinder reproductive health outcomes.
Preventive Measures to Combat Obesity:
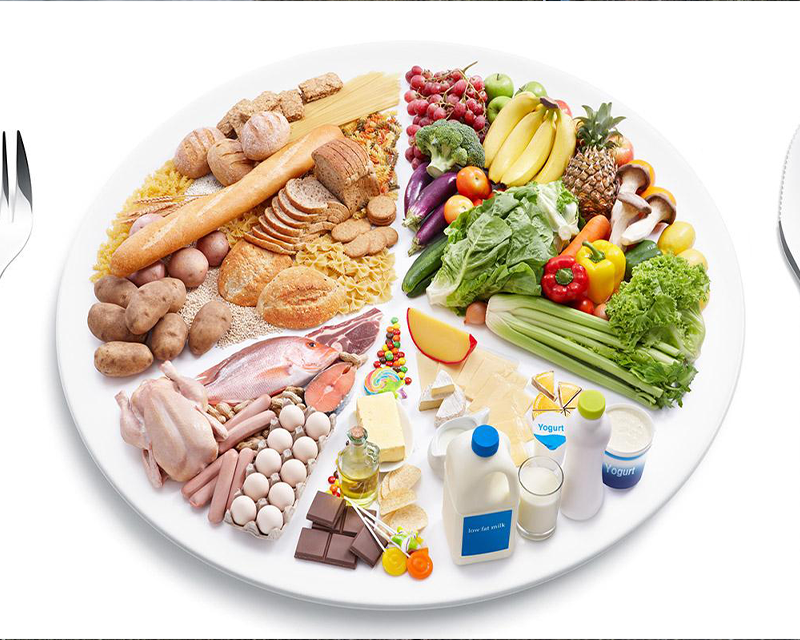

To combat obesity, the most crucial step is to adopt a balanced and healthy diet. This includes incorporating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your meals while limiting the intake of sugary beverages, processed foods, and high-fat treats. It is also beneficial to practice portion control and mindful eating to avoid overconsumption of calories.
Regular physical activity plays a vital role in preventing and managing obesity. Aim to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Incorporating strength training exercises a few times a week can help build muscle mass and boost metabolism, aiding in weight management. Remember that consistency is key when it comes to maintaining a healthy weight and overall well-being.