Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) are neurodevelopmental disorders that can often present with overlapping symptoms, leading to potential confusion in diagnosis.
However, there are key differences between the two conditions that set them apart. ADHD is characterized by symptoms of impulsivity, hyperactivity, and inattention, which can impact a person's ability to focus, organize tasks, and regulate their behavior in various settings. On the other hand, Autism is marked by challenges in social communication and interaction, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors that can affect how individuals perceive and respond to the world around them. Understanding these core distinctions is essential for accurate assessment and tailored intervention strategies to support individuals with these conditions.
ADHD and Autism: Common Symptoms and Characteristics:
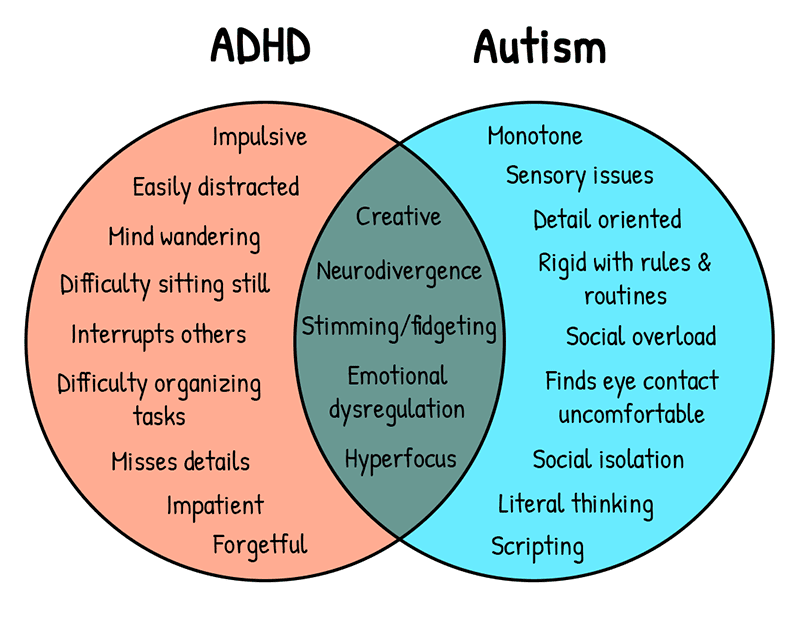
- Individuals with ADHD often exhibit symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
- They may struggle to stay focused on tasks, have difficulty organizing activities, and often act before thinking.
- Additionally, restlessness, fidgeting, and challenges in following instructions are commonly observed characteristics in individuals with ADHD.
- On the other hand, individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) frequently display challenges in social communication and interaction.
- They may have difficulties in understanding nonverbal cues, maintaining eye contact, and engaging in reciprocal conversations.
- Moreover, repetitive behaviors, restricted interests, and sensory sensitivities are common traits seen in individuals with autism.

ADHD and Autism: Diagnosis and Evaluation:
A thorough and comprehensive evaluation is crucial when it comes to diagnosing ADHD and Autism. Assessments typically involve gathering information from multiple sources, including parents, teachers, and other caregivers, along with direct observation of the individual's behavior. Various standardized tools and questionnaires are often used to assess symptoms and behaviors associated with ADHD and Autism, helping clinicians make an accurate diagnosis.
In addition to behavioral assessments, medical professionals may also conduct physical exams and neurological evaluations to rule out any underlying medical conditions that could be contributing to symptoms. Psychological testing may be utilized to further evaluate cognitive and social functioning, providing valuable insights into the individual's strengths and challenges. Overall, a comprehensive evaluation process is essential in determining an accurate diagnosis of ADHD and Autism, paving the way for appropriate treatment and support interventions.
ADHD and Autism: Treatment Approaches and Strategies:

When it comes to treating ADHD and autism, a multimodal approach is often recommended. This approach may include behavioral interventions, medication management, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and social skills training. Each individual's treatment plan should be tailored to their specific needs and may evolve over time as new strategies are introduced or adjusted.
Behavioral interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) can be beneficial in addressing behavioral challenges associated with ADHD and autism. These interventions focus on teaching individuals new skills, reducing problem behaviors, and improving overall functioning. Medications, such as stimulant medications for ADHD or atypical antipsychotics for autism, may also be prescribed in some cases to help manage specific symptoms. It is important for families and healthcare providers to work together to regularly assess the effectiveness of treatments and make adjustments as needed.
ADHD and Autism: Challenges in School and Social Settings:

Challenges in school and social settings can be significant for individuals with ADHD and autism. In school, children with ADHD may struggle with maintaining focus, following instructions, and staying organized. They may also experience difficulties with time management and completing tasks. These challenges can lead to academic underachievement and frustration for both the students and their teachers.
Similarly, individuals with autism may have trouble with social interactions and communication in school settings. They may find it challenging to understand social cues, make friends, and engage in group activities. The rigid routines and sensory sensitivities often associated with autism can also create obstacles to navigating the social dynamics of school environments. Additionally, transitions between activities or changes in routine can be particularly challenging for individuals with autism, leading to feelings of anxiety and distress.
ADHD and Autism: Cognitive and Behavioral Differences

Individuals with ADHD often exhibit impulsivity, hyperactivity, and inattention. They may struggle with staying focused on tasks, following instructions, and organizing their thoughts. On the other hand, individuals with autism may display repetitive behaviors, difficulties with social interactions, and challenges in understanding nonverbal cues.
Cognitively, individuals with ADHD may have issues with working memory, leading to forgetfulness and difficulty with multitasking. In contrast, individuals with autism may excel in certain areas of cognitive functioning, such as pattern recognition and attention to detail, while facing challenges in abstract thinking and flexible problem-solving.
ADHD and Autism: Neurodevelopmental Factors
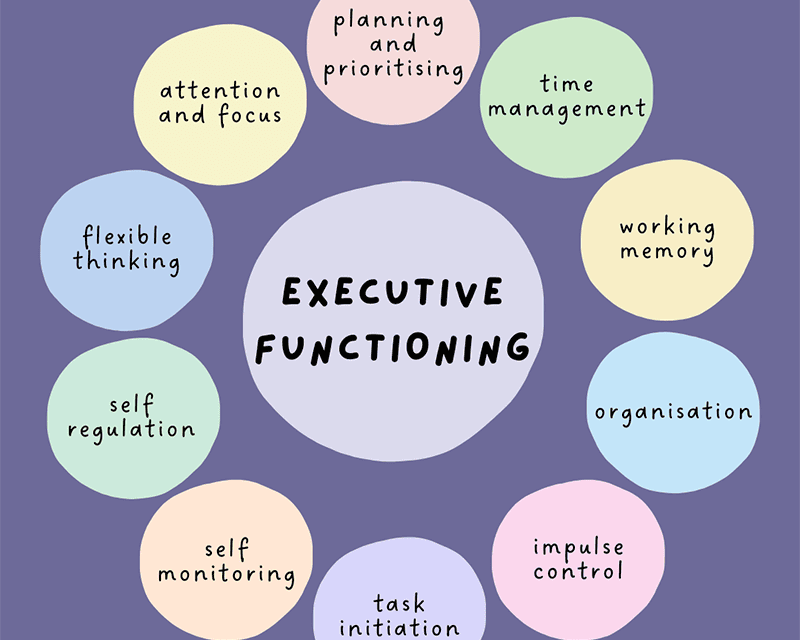
Neurodevelopmental factors play a crucial role in shaping the unique profiles of individuals with ADHD and autism. In ADHD, research suggests that there may be differences in the development of certain brain regions involved in executive functioning and attention regulation. These differences can contribute to challenges in impulse control, sustained attention, and organization skills that are commonly observed in individuals with ADHD.
On the other hand, in autism, neurodevelopmental factors are thought to involve atypical connectivity patterns in the brain, particularly affecting areas responsible for social cognition and sensory processing. These differences can lead to difficulties in social interactions, communication, and sensory sensitivities in individuals with autism. Understanding these neurodevelopmental factors is essential for tailoring interventions and support strategies that address the specific needs of individuals with ADHD and autism.
ADHD and Autism: Genetic and Environmental Influences

Genetic and environmental influences play significant roles in the development of both ADHD and autism. Genetic factors have been found to contribute to the likelihood of developing either condition, with certain genes being associated with an increased risk. Studies have also indicated a strong hereditary component, where individuals with a family history of ADHD or autism are more likely to be affected.
In addition to genetic factors, environmental influences can also impact the manifestation of ADHD and autism. Prenatal exposure to certain toxins, maternal smoking during pregnancy, and early life stressors have been linked to an increased risk of developing these neurodevelopmental disorders. Furthermore, factors such as access to early intervention services, socio-economic status, and parental involvement can also play a role in the expression of symptoms and overall outcomes for individuals with ADHD and autism.
ADHD and Autism: Comorbidity and Co-occurrence
Individuals with ADHD and Autism often experience comorbidity and co-occurrence of symptoms, which can present unique challenges for diagnosis and treatment. Given the overlap in symptoms between the two conditions, such as difficulties in social interactions and impulsivity, it can be complex to accurately differentiate the primary diagnosis and address specific needs effectively. Research indicates that up to 78% of individuals with Autism also meet the criteria for ADHD, highlighting the high prevalence of comorbidity between these neurodevelopmental disorders.
Furthermore, the presence of both ADHD and Autism can intensify behavioral issues, communication difficulties, and sensory sensitivities in individuals, impacting their overall daily functioning and quality of life. The co-occurrence of these conditions may also result in additional barriers to accessing appropriate support and interventions, as strategies tailored to address the unique needs of each condition may be required. Understanding the interconnected nature of ADHD and Autism in terms of comorbidity and co-occurrence is crucial for providing comprehensive care and enhancing outcomes for individuals facing these complex challenges.
ADHD and Autism: Impact on Daily Functioning
Individuals with ADHD often struggle with daily functioning due to difficulties with attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. These challenges can impact various areas of life, such as work, school, and relationships. For example, maintaining focus on tasks can be a significant challenge, leading to decreased productivity and increased frustration. Impulsivity may also result in poor decision-making and difficulties in social interactions. Hyperactivity can make it challenging to sit still for extended periods, affecting tasks that require sustained attention.
Similarly, individuals with autism may experience difficulties in daily functioning, primarily related to social communication and repetitive behaviors. Social interactions can be particularly challenging, as individuals with autism may struggle to understand social cues and engage in reciprocal communication. Repetitive behaviors and routines can also impact daily activities, causing distress when routines are disrupted. These challenges in daily functioning can lead to difficulties in forming and maintaining relationships, succeeding in academic or work environments, and navigating everyday tasks independently.
ADHD and Autism: Support and Resources for Individuals and Families
Individuals with ADHD and autism, as well as their families, often benefit from a wide array of support and resources tailored to their specific needs. These resources can include educational programs that focus on skill development, behavioral therapies to address social challenges, and counseling services to help navigate daily struggles and emotional well-being. Support groups and community organizations also play a vital role in providing a network of understanding and empathy for individuals and families facing the complex realities of ADHD and autism.
In addition to professional services, online resources and informational websites offer valuable tools and guidance for individuals and families seeking to better understand and manage ADHD and autism. These platforms provide access to the latest research, treatment options, and practical tips for improving daily functioning and quality of life. By empowering individuals and families with knowledge and support, these resources play a crucial role in fostering resilience, advocacy, and a sense of community among those affected by ADHD and autism.